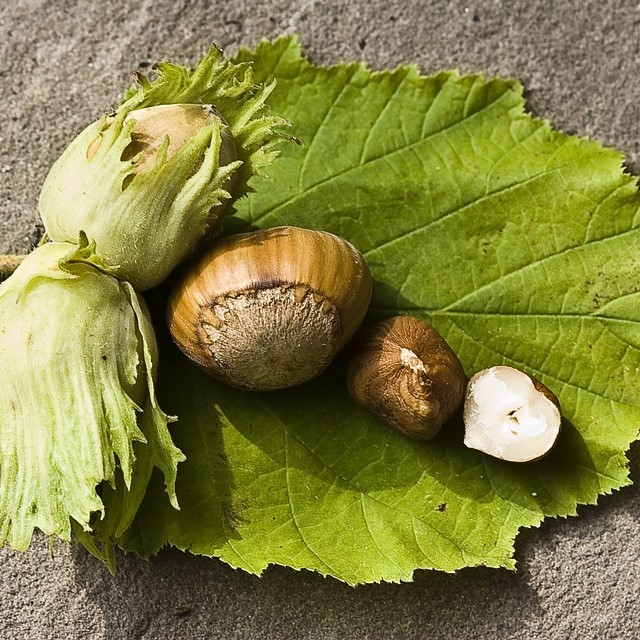
Hazelnut
Corylus americana
92 reviews
Hazelnut
Corylus americana
92 reviews
3.5 Gallon
We are sorry, product is currently out of stock due to seasonal availability. Please check the "Related plants available in your area" section below
Not just beautiful - intentionally selected by ShrubHub's 3D landscape design team to fit real-world spaces and maximize yard potential.
Why Hazelnut?
Hazelnut (Corylus americana) is a deciduous shrub native to North America. It is highly valued for its tasty, nutritious nuts and is widely cultivated for commercial purposes. Hazelnuts are rich in healthy fats, vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. They have a unique nutty flavor and are used in various culinary dishes, desserts, and as a popular ingredient in chocolates and spreads like Nutella.
Sunlight
Hazelnut trees require full sun exposure for at least 6-8 hours per day to thrive and produce an abundant harvest of nuts.
Watering
Hazelnut trees generally require regular watering during the first few years after transplantation. Mature hazelnut trees, however, are generally drought-tolerant and require less frequent watering, especially when established in well-drained soil.
Fertilizing
The fertilizer requirement for Hazelnut depends on various factors like soil condition, nutrient levels, and previous fertilization. A soil test is recommended to determine specific fertilizer needs and ensure optimal growth and yield.
Hazelnut (Corylus americana)
The Hazelnut, scientifically known as Corylus americana, is a small deciduous tree native to North America. It is best known for its delicious and nutritious nuts that are highly valued for both culinary and commercial purposes.
The Hazelnut tree typically grows up to 20 feet in height, with attractive oval-shaped leaves that turn yellow in the autumn. It produces small clusters of flowers in early spring, which eventually develop into rounded or oval-shaped nuts enclosed in a hard, woody shell.
These nuts are not only tasty but also packed with essential nutrients. Hazelnuts are a rich source of healthy fats, fiber, protein, and various vitamins and minerals. They are especially high in vitamin E and B vitamins, which promote healthy skin, hair, and overall well-being.
Hazelnuts are widely used in culinary applications due to their distinctive flavor and versatility. They can be consumed raw, roasted, or ground into a flour-like consistency, adding a delightful nutty taste to desserts, baked goods, chocolates, spreads, and even savory dishes like salads and roasted vegetables.
Aside from their culinary value, Hazelnuts also have several health benefits. These nuts have been associated with reducing the risk of heart disease, improving brain health, and aiding in weight management. Additionally, they contain antioxidant compounds that help protect against cellular damage caused by oxidative stress.
When purchasing Hazelnuts, it is essential to select ones that are fresh, with a crisp texture and a creamy color. They should be stored in an airtight container in a cool, dry place to maintain their freshness and prevent spoilage.
Whether you enjoy them as a snack, use them in cooking and baking, or incorporate them into a balanced diet, Hazelnuts offer a delightful combination of flavor, versatility, and health benefits.
Plant Information:
| Botanical Name: | Corylus americana |
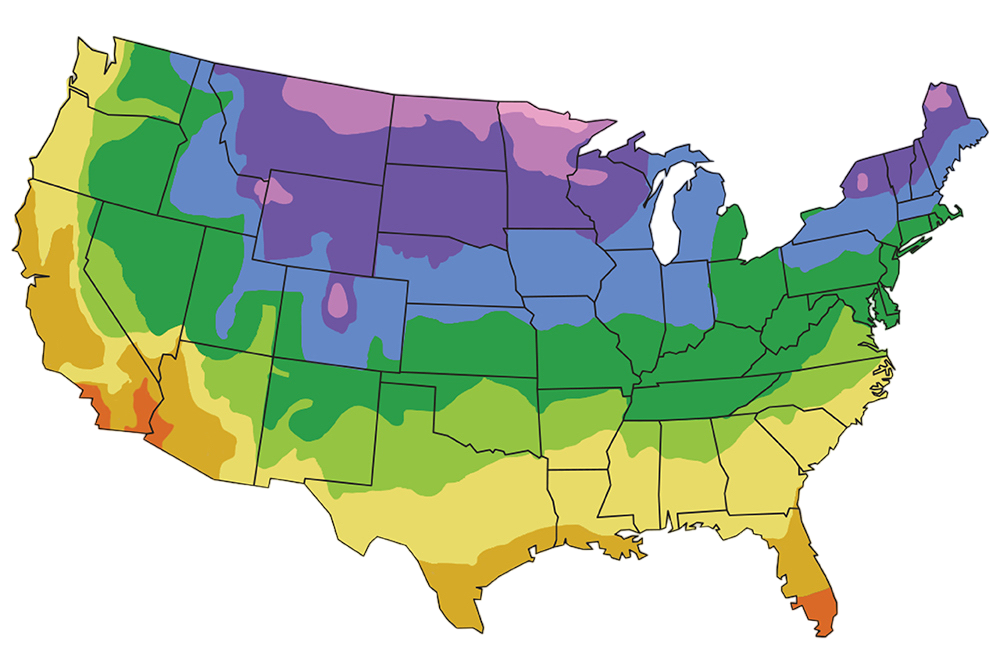
| USDA Zones: | 4 - 9 |
| Water: | Moderate |
| Exposure: | Full Sun |
| Soil Needs: | Widely Adaptable |
| Mature Height: | 8 - 15 feet |
| Mature Spread: | 8 - 15 feet |
Pollination Info
Pollination Information for Hazelnut (Corylus americana)
The hazelnut tree, scientifically known as Corylus americana, is an important commercial crop that relies on proper pollination for successful fruit production. Here are some key details about its pollination:
1. Pollination Method
Hazelnut trees primarily depend on wind pollination. They possess both male and female flowers on the same tree, making them monoecious plants. However, they are largely self-incompatible, meaning that they cannot reliably self-pollinate.
2. Pollination Period
The pollination period for hazelnuts usually takes place in early spring when the male flowers (catkins) release pollen. This timing coincides with the emergence of the female flowers (small reddish tufted structures called styles) and the development of receptive stigmas.
3. Pollination Requirements
Hazelnuts require cross-pollination by wind, which involves the transfer of pollen from the male flowers to the female flowers of a different hazelnut tree. Therefore, it is crucial to have compatible hazelnut cultivars planted in close proximity to ensure successful pollination and fruit set.
4. Pollinators
While hazelnuts primarily rely on wind for pollination, certain insect pollinators such as bees and other flying insects can enhance pollination efficiency. These insects accidentally pick up and transfer hazelnut pollen while foraging for nectar or pollen from other flowering plants. Encouraging a diverse population of pollinators in the vicinity of hazelnut orchards can enhance fruit set.
5. Hazelnut Orchard Design
To maximize pollination and fruit yield, hazelnut orchards should be carefully planned and designed. Planting different hazelnut cultivars with overlapping flowering times is essential for cross-pollination. Orchards should also have rows oriented perpendicular to prevailing winds to facilitate effective pollen movement between trees.
6. Environmental Factors
Environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, and wind speed can influence hazelnut pollination. Conditions that favor good pollen dispersal, such as moderate temperatures and slight breeze, will enhance pollination success.
By considering these pollination factors, hazelnut farmers and cultivators can optimize fruit set and improve overall yield in their orchards.
FAQ
Hazelnut (Corylus americana) FAQ
General Information
Q: What is Hazelnut (Corylus americana)?
A: Hazelnut, scientifically known as Corylus americana, is a deciduous shrub that belongs to the birch family Betulaceae. It produces edible nuts and is commonly found in North America.
Q: What are the common names for Hazelnut?
A: Hazelnut is also known by various common names such as American hazelnut, American filbert, and wild hazelnut.
Q: What are the characteristics of Hazelnut plants?
A: Hazelnut plants are generally multi-stemmed shrubs that can grow up to 12-20 feet in height. They have round-to-oval-shaped leaves and produce catkins in early spring.
Cultivation
Q: What are the ideal growing conditions for Hazelnut?
A: Hazelnut plants prefer well-drained soil with a pH ranging from 6.0 to 7.5. They thrive in full sun to partial shade and require a moderate amount of water.
Q: Can Hazelnut withstand cold temperatures?
A: Yes, Hazelnut plants are hardy and can tolerate cold temperatures. They are adapted to USDA hardiness zones 4-9.
Q: How long does it take for Hazelnut to produce nuts?
A: It usually takes about 3-5 years for Hazelnut plants to start producing nuts after planting.
Pruning and Maintenance
Q: When is the best time to prune Hazelnut plants?
A: It is recommended to prune Hazelnut plants in late winter or early spring when they are dormant. This helps to stimulate new growth and maintain the desired shape.
Q: How often should I fertilize Hazelnut?
A: Hazelnut plants benefit from annual fertilization. Apply a balanced fertilizer in early spring before or during bud break.
Q: Are there any common pests or diseases that affect Hazelnut plants?
A: Yes, Hazelnut plants are susceptible to pests such as aphids, mites, and filbertworms. They can also be affected by diseases like Eastern filbert blight and crown gall. Regular monitoring and appropriate control measures can help manage these issues.
Harvesting and Uses
Q: When are Hazelnuts ready to be harvested?
A: Hazelnuts are usually ready for harvest in late summer or early fall. The nuts should be mature and easily come off the tree.
Q: What are some popular uses for Hazelnuts?
A: Hazelnuts have a variety of culinary uses. They are commonly used in baking, confectionery, and as ingredients in spreads like Nutella. They can also be eaten raw or roasted for snacking.
Q: Are there any health benefits associated with consuming Hazelnuts?
A: Yes, Hazelnuts are a good source of healthy fats, fiber, and various vitamins and minerals. They are known to promote heart health, help manage blood sugar levels, and support overall well-being when consumed as part of a balanced diet.
Planting & Care
Hazelnut (Corylus americana) Planting & Care Guide
Planting:
- Choose a location with full sun to partial shade.
- Ensure the soil is well-draining and rich in organic matter.
- Dig a hole that is twice the diameter and depth of the root ball.
- Place the hazelnut sapling into the hole, making sure the top of the root ball is level with or slightly above the ground surface.
- Backfill the hole with soil, gently firming it around the base of the plant.
- Water thoroughly after planting to settle the soil.
Care:
- Watering: Keep the soil consistently moist, especially during dry spells. Avoid overwatering, as hazelnut trees dislike waterlogged conditions.
- Pruning: Prune hazelnut trees during late winter or early spring to remove dead or diseased branches. Maintain an open center shape by removing crossing branches and encouraging good air circulation within the canopy.
- Fertilization: Apply a balanced fertilizer in early spring before new growth begins. Follow package instructions for proper application rates.
- Mulching: Apply a layer of organic mulch around the base of the tree, leaving a gap around the trunk to prevent rot. Mulch helps retain soil moisture and suppresses weed growth.
- Pest and Disease Control: Monitor your hazelnut tree regularly for signs of pests such as aphids, caterpillars, or mites. Use appropriate organic or chemical control methods if necessary. Watch out for diseases like Eastern filbert blight, and promptly remove infected plant parts.
- Harvesting: Hazelnuts typically mature in late summer or early fall. Harvest nuts when they have fallen naturally from the tree, or shake the tree gently to encourage ripe nuts to drop. Remove the husks and allow the nuts to dry completely before storing or consuming.
Following these planting and care guidelines will help ensure healthy growth and a bountiful harvest of hazelnuts from your Corylus americana tree.
Check Out These Verified Customer Reviews:
Customer Reviews
4.7 out of 5 based on 92 reviews
Thank you! Your review has been submitted.
The shipment was fast and the hazelnuts were well-packaged.
Delicious hazelnut flavor
Easy website navigation
Item has been added to your cart.